
- #Uranium nuclear fission equation full#
- #Uranium nuclear fission equation plus#
- #Uranium nuclear fission equation series#
In one experiment, a thin sheet of uranium was placed inside a cloud chamber. For example, a cloud chamber is a device in which vapor trails of moving nuclear particles can be seen and photographed. Scientists in the United States and elsewhere quickly confirmed the idea of uranium fission, using other experimental procedures. It takes only a small amount of energy to start the vibration which leads to a major breakup. Meitner named this process “fission ” because it is similar to the process of cell division in biology. If the vibration is violent enough, the drop can break into two pieces. When an extra neutron enters, the drop begins to vibrate. One can visualize the uranium nucleus to be like a liquid drop containing protons and neutrons.

Lise Meitner (1878 –1968), a long –time colleague of Hahn who had left Germany due to Nazi persecution, suggested a helpful model for such a reaction. It was very puzzling to them how a single neutron could transform element 92 into element 56. Hahn and Strassmann published a scientific paper showing that small amounts of barium (element 56) were produced when uranium (element 92) was bombarded with neutrons. The evidence for this supposed process came from chemical analysis. The uranium nucleus apparently underwent a major disruption. When uranium was bombarded with neutrons, however, an entirely different reaction seemed to occur. Other elements became radioactive in the same way. If they bombarded copper, for example, a radioactive form of copper was produced.
#Uranium nuclear fission equation series#
They had been doing a series of experiments in which they used neutrons to bombard various elements. The fission reaction was discovered in l938 by two German scientists, Otto Hahn (1879 –1968) and Fritz Strassmann (1902 –1980). Reactors are utilized for production of electricity at nuclear power plants, for propulsion of ships and submarines, and for the creation of radioactive isotopes used in medicine and industry. After the war, controlled energy release from fission was applied to the development of nuclear reactors. The fission reaction was the basis of the atomic bomb, which was developed by the United States during World War II. Fission fragments were shown to fly apart with a large release of energy.
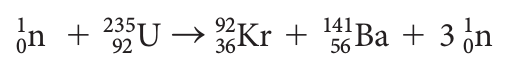
This reaction was discovered when a target of uranium was bombarded by neutrons. Nuclear fission when the nucleus of an atom splits, usually into two pieces. The controversy about nuclear power plants If you’re looking for more help with IB Chemistry, including hints for your IA, then be sure to visit our Chemistry subject page where you’ll find more articles, study tools, and other resources.Nuclear reactors for electric power production A table of contents for the book as well as some sample pages are available through the link below. If you’re looking for practice questions on this topic or more succinct explanations of key concepts in IB Chemistry Option C, then pick up a copy of our study guide. This quick review of nuclear fusion and fission has hopefully helped to reinforce your understanding.

Expanding your IB Chemistry Option C: Energy knowledge You do not need to learn any specific nuclear equations but you do need to be able to deduce mass numbers and atomic numbers or the name of the elements for the nuclei involved, if given enough information. In your exam you might be set problems ‘ balancing’ these nuclear equations. Nuclear fusion occurs when two very light nuclei (such as hydrogen) combine together to make a larger nucleus.Įnormous heat and pressure are required to overcome the electrical repulsion of protons but there is a net release of energy in the process. There are two ways this can happen: nuclear fusion and nuclear fission. Nuclear energy is energy that is released when atomic nuclei change.
#Uranium nuclear fission equation plus#
The guide also contains over 25 practice questions plus four exam-style questions to allow you to test your knowledge and understanding.
#Uranium nuclear fission equation full#
The study guide is full of concise, easy-to-understand explanations of complicated concepts that can help you stay on top of your IB Chemistry Option C studies. If you’re studying IB Chemistry Option C: Energy then this straightforward explanation of nuclear fusion and nuclear fission extracted from our IB study guide, Chemistry Option C: Energy Standard and Higher Level written by Tony Hickling, is for you. IB Chemistry is known for being a challenging subject, so we’ve pulled some useful explanations of key concepts from our study guides to help make your revision a bit easier.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
